Abbreviation ASCII it means American Standard Code for Information Interchange. ASCII is a Unicode that allows you to encode characters. Among other things, the code can be used for URL encoding. ASCII is a 7-bit code. It was made public for the first time in 1963 and in its final version in 1968.
Structure
A single character, be it a letter, digit, or HTML special character, is represented as a number sequence between 00 and 255. This can be represented using 8 bit. Regardless, it is no longer the classic seven-bit ASCII sequence.
Character sets
Different sets of characters can be encoded. The default character set, which is always the same, has the values of 32 to 127. Contains the uppercase and lowercase alphabet, as well as Arabic numerals and punctuation. Values 00-31 are non-printable control characters, and the rest are typically dedicated to special characters like î, é, or €. Special characters like the German ß or umlauts like ü, ä and ö are possible thanks to the eighth bit, which arose later. The task may be different.
Currently the Unicode UTF-8 it has replaced the original ASCII code, since it can represent all the characters of human languages using 8 bits.
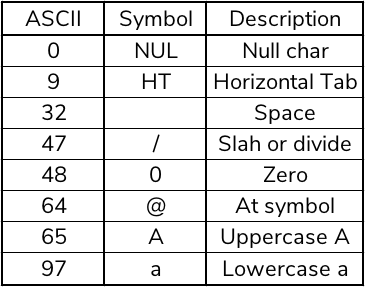
ASCII table
The characters assigned to the code number appear in a table and can be accessed, for example, in ascii-code.com.
Examples
ASCII code and SEO
ASCII characters are currently used to make search snippets attractive. Checkmarks, stars, or other characters are stored in meta descriptions and displayed in search results. In this way, the user's attention can be directed specifically to the search results, which can have a higher CTR result.
ASCII art
Using different character strings, computer artists create images that are also called ASCII art. Real photos can, for example, be rewritten into ASCII images by means of programs[1].
References