The OnPage optimization It covers all the changes that are carried out in the web portal: measures related to the content, with the structure of the web portal, among many other technical factors. It all starts with the selection of keywords to get a better ranking in the SERPs. At the same time, the content, in the form of texts, images and videos, must be interesting and relevant. If all this takes place, Googlebot (Google robots) will recognize the topic of each content and analyze the relevance of the selected keywords.
The structure of a web portal depends on its internal links. There are also technical factors such as site maps XML sitemaps, the control of the trackers by means of the Robots.txt files and the canonical tag. The canonical tag helps avoid the negative effects of duplicate content. Finally, aspects such as the usability, the design and performance of a web portal.
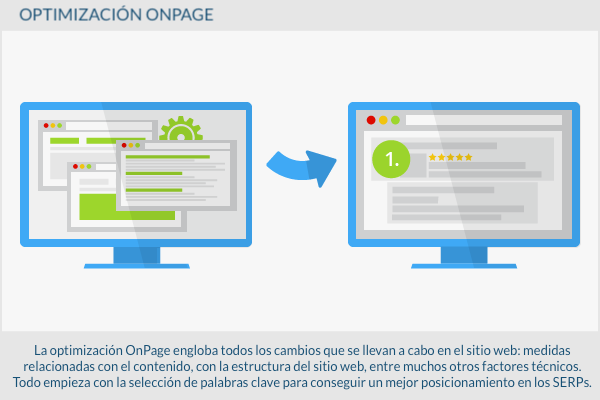
The OnPage optimization must run in parallel to the OffPage optimization since the creation of external backing links, Backlink, without respective landing pages it is not efficient.
Importance
Constant monitoring is required so that the web portal maintains a good positioning in a stable and long-term manner.
Because search engines do not show which algorithms they use to rank a web portal, there are no standard guidelines for perfect optimization. However, not only the web portal as such must be optimized, but also each and every one of its pages. There are numerous advisable practices that can be carried out to create added value on your web portal.
Below, you will find a list of fundamental tips to get a good position from an SEO expert.
Url
Length
Usually the length of the URL does not count as a factor for ranking. However, it is essential for search engines as it can make it easier / harder for crawlers to analyze. Experience shows that short URLs tend to receive more visits than long ones. At the same time, due to its simplicity, a short URL is more likely to be linked on other websites, recommended via email, or disclosed verbally.
Keyword positioning
The more similarity there is between a web portal domain and a keyword, the better ranking that particular web portal will get for that keyword. For example, the web portal “website.com/keyword” will obtain a better positioning than the web “website.com/subpage1/subpage2/keyword”.
Word separation
The hyphen is still the preferred symbol for separating keywords from URLs. Despite the fact that search engines claim that the low bar is treated the same, experience shows that the use of the middle dash appears to be preferred.
HTML header
Title
The title tag, also known as Goal Title, is probably the most important element of a web portal since it is used as a headline in search results. Studies show a clear link between the position of a keyword in the title and the positioning of the web portal. Positioning the keyword correctly at the beginning of the title gives a better result than placing it elsewhere. This is why, the selection of the keyword, or a combination of them, and its position in the title should be considered priority factors of the optimization of your web portal.
Meta description tag
The label of the Goal Description it does not affect positioning. However, it affects the traffic and popularity of the web portal. Appears as Snippets, short summary, of the web portal in the search results and shows a brief description of the web and its content. It is recommended to emphasize the keywords by showing them in bold and include them in the snippet to generate interest in the user.
Canonical label
The canonical tag It is primarily useful for very large websites. With a large number of people participating in the same project and with many different pages, it is not difficult for the same content to be published several times and to worsen the positioning of the web portal. With the Rel = Canonical tag, search engines index the URL set as standard, or original source, and don't pay as much attention to duplicate content.
HTML Body
Synonyms
In one of these videos, Matt Cutts, Director of Webspam, answers the question of whether or not keyword synonyms should be included in the text. In general, it recommends the use of synonyms but without exaggeration. The genuineness and readability of a text should always be the main objective. Matt adds that Google has its own synonym experts who teach search engines about paraphrasing. However, webmasters shouldn't spend too much time on it to be able to focus on the originality and quality of the content.
Header tag
The header tag, Heading Tag in English (from h1 to h6 in HTML), it allows browsers, search engines and screen readers to recognize headings, and search engines use these tags to identify keywords related to texts. That is why it is also advisable to use keywords in the heading tags.
ALT attribute
The ALT attribute It is used to attach alternative texts to digital media such as images and videos. These alternative texts are essential since search engines cannot process this type of information. At the same time they are necessary so that readers of texts for the blind can read this content and users with visual disabilities can understand the content of the images. The ALT attribute has been shown to be associated with the positioning of a web portal. For this reason, it is recommended to include an image or any other digital communication medium on each and every page and use keywords in the ALT attribute. IMPORTANT: excessive use implies penalties.
Name of the image
Image search also generates traffic on the web portal. Therefore, all images must have a relevant title that contains a keyword.
In bold / italic
Both in bold and in italics, the keywords in a text are always related to the positioning of a web portal. For this very reason, it is recommended to indicate the meaning of a text with keywords, or a combination of them, and offer added value to readers.
Internal links
Click Depth
The length of the user's navigation path on the web portal, or Click Depth, describes how many clicks need to be made to get from the home page to the landing page. Each link that does not link to the home page is called Deep Link, deep link. The longer it takes to navigate through the web, the greater the Click Depth. From an SEO point of view, it is recommended to keep this path short to facilitate accessibility to users and search engines.
Even though the pages of the web portal are usually found when browsing, it is also feasible to indicate the next page through internal links. This internal link structure has a positive effect on the positioning of the web portal. However, it should not be forgotten that Google probably only scores the first link of a page present in the HTML code.
Web Links
- SEO Onpage basics Blog ninjaseo.es
- SEO On Page. Steps for your website to surprise Google Blog luismvillanueva.com
- How to make a website optimized for SEO Blog 40defiebre.com
- SEO ON PAGE: THE DEFINITIVE GUIDE TO OPTIMIZE YOUR WEB Blog tesubi.com