We have proposed to create this article as a guide to learn what all the components of a PC, absolutely explained and with the maximum possible detail. So anyone who does not know precisely what a PC consists of or what parts we can find inside, from now on you will not have excuses.

<>
Thousands of reviews, hundreds of news and a lot of tutorials are what we carry behind us, and the time had not yet come to create a post orientado a los que se están iniciando en el mundo de la informática and the PCs to provide them with the basic knowledge of which are the components of a PC and what function each one of them fulfill.
With this guide, we want those who know less about PCs to get a fairly complete idea of what components are there and the latest trends today, so you know how to start building your own computer.
Internal components and peripherals

In a PC, there are two large groups of electronic components, internal and peripherals. But what we really call PC is the grouping of internal components inside a chassis or computer case.
Los componentes internos son los que componen el hardware de nuestro equipo, y serán los encargados de manejar la información que nosotros introducimos o la que descargamos desde Internet. They will be the ones that will make it possible for us to store data, play games or show the work we do on a screen. The basic internal components will be:
- Base plate
- CPU or processor
- RAM
- HDD
- Graphic card
- Power supply
- Network card
These components are going to generate heat, since they work through electricity and at enormous processing frequencies. Then we also consider internal components the following:
- Heatsinks
- Fans
- Liquid refrigeration
Well, somewhere we will have to start, and what better way to do it than by looking at each of the components that are installed inside a PC, or where appropriate, those that will be critical and basic.
CPU or microprocessor
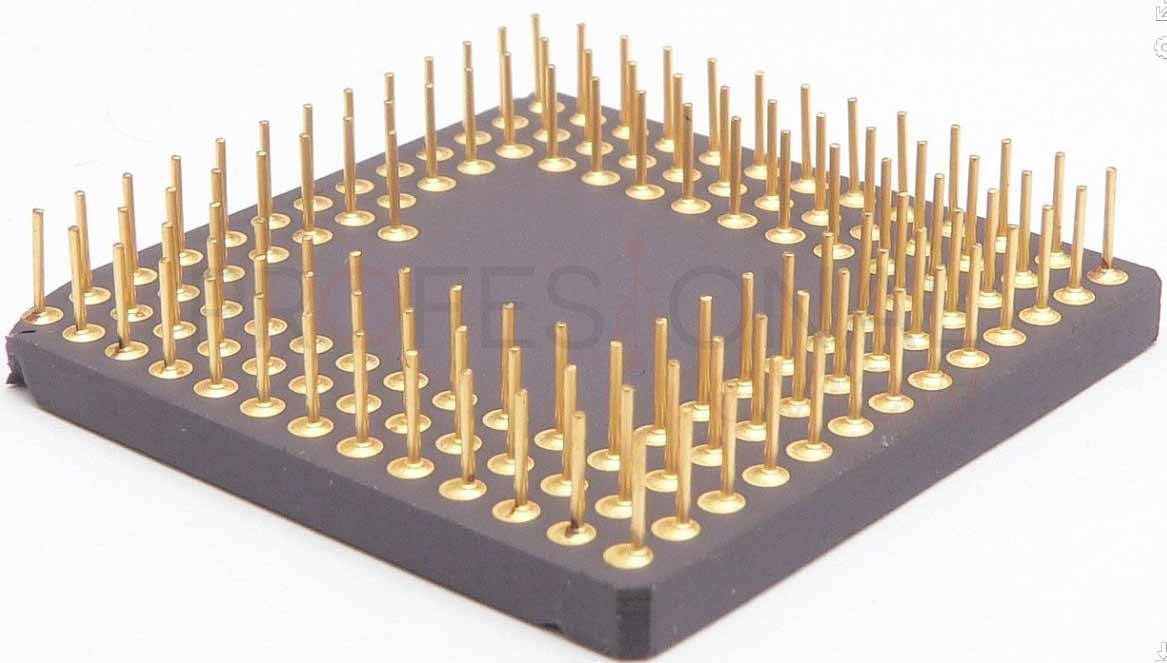
The microprocessor It is the brain of the PC, the one that is responsible for completely analyzing all the information that passes through it in the form of ones and zeros. The processor decodes and executes the instructions of the programs loaded into the main memory of the PC and coordinates and controls all or almost all componentsas well as connected peripherals. The speed with which a CPU processes these instructions is measured in cycles per second or hertz (Hz).
The CPU is nothing but a hell of a complex silicon chip in which there are millions of transistors and integrated circuits installed in it together with a series of pins or contacts that will be connected to the motherboard socket.
At the same time, the new CPUs on the market not only have one of these chips physically speaking, but also have several units inside called Nuclei or Cores. Each of these nuclei will be able to process one instruction at the same time, thus being able to process as many simultaneous instructions as cores have a processor.
What is measured in a processor to understand if it is good
It happens to know if a processor is powerful or notWhat we always have to measure is the frequency at which it works, in other words, the number of operations it is capable of performing per unit of time. But at the same time of this measure, there are others that are also fundamental to know its performance and be able to compare it with other processors:
- Frequency: at this time it is measured in Gigahertz (GHz). A microprocessor has a clock inside that marks the number of operations that it will be able to do. The more frequently, the more of them.
- Bus width: in a simple way, it marks the work capacity that a processor has. Mientras más ancho be este bus, más grandes serán las operaciones que podrá hacer. Current processors are 64 bits, in other words, they can do operations with strings of 64 consecutive ones and zeros.
- Memory Cache: the more cache memory the processor has, the more instructions we will be able to save in them to catch them quickly. Cache memory is much faster than RAM and serves to save the instructions that are going to be immediately used.
- Processing cores and threads: And the more cores and processing threads, the more operations we will be able to do simultaneously.
Microarchitecture and manufacturers

Another thing that we must know about this component are the manufacturers what is there at the moment and the architecture which is on the market. We simply have two manufacturers of computer processors, each with its own architecture.
The architecture of a microprocessor is formed by instruction set with which a processor is manufactured, at the moment the x86 predominates. You will have seen this number on most CPUs. At the same time as this, architecture indicates to us the manufacturing procedure and size used to implement the transistors.
Intel:
Intel is a manufacturer of integrated circuits and is the one that invented the x86 series of processors. The current architecture of this manufacturer is the x86 with transistors 14 nm (nanometers). At the same time, Intel names each of its updates by a codename and a generation. Today we are in the 9th generation of named processors Coffee lake, predecessor of Kaby lake and Kaby Lake R in addition to 14 nm. It will soon launch the first processors of 10 nm Cannon Lake.
AMD:
Intel's other direct rival processor manufacturer is AMD. It also uses the x86 architecture for its processors and in the same way that Intel also names its processors with a code name. AMD is currently with processors of 12 nm with architecture name Zen + and Zen2 and models Ryzen. In a short period of time we will have the new architecture 7nm Zen3.
Base plate
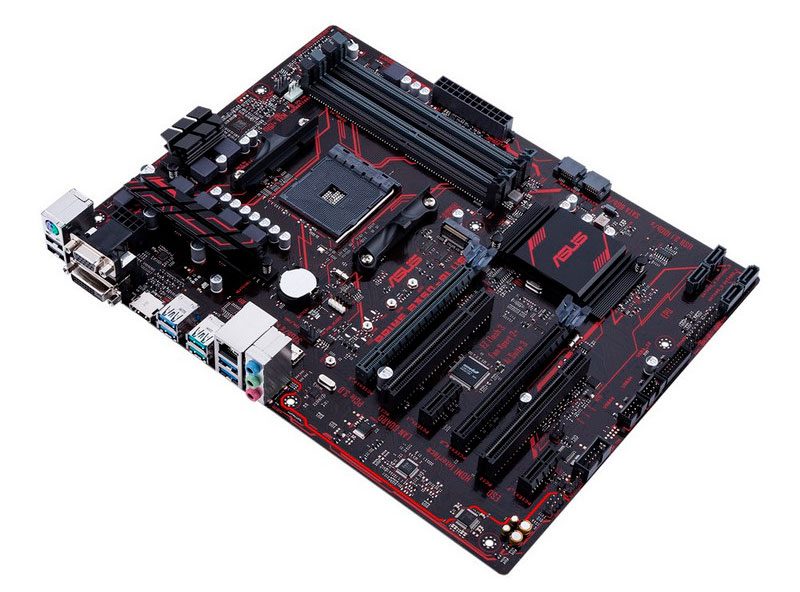

Although the CPU is the heart of our PC, it could not function if the motherboard did not exist. A motherboard is simply a PCB board made up of an integrated circuit that interconnects a series of chips, capacitors and connectors scattered throughout it, which as a whole forms the PC.
On this board we will connect the processor, the RAM the Graphic card and practically all the internal items of our PC. Clarifying a motherboard in detail is tremendously complex due to the huge number of important items it has.
What we really must understand about a motherboard is that going to set the processor architecture that we can install in it, at the same time as other components such as RAM. Since not all are the same and each one is oriented to certain processors.
Motherboard formats

A fundamental aspect of a motherboard is its shape or format, since the number of expansion slots and the chassis that will support it will depend on this.
- XL-ATXand E-ATX: these are special formats and involve the acquisition of a large tower with 10 or more expansion slots. They are ideal for mounting full liquid cooling, multiple graphics cards, and many storage drives.
- ATX: Your measurements are regularly 30.5 cm x 24.4 cmAnd it is compatible with the 99% of computer cases on the market. It is our recommended format in all our Gamer configurations or for Workstation equipment.
- Micro-ATX: Have a smaller size, very common, but with the arrival of smaller motherboards it has been a little out of place. Ideal for salon teams.
- ITX: His arrival has revolutionized the world of motherboards and gaming equipment with truly small dimensions and capable of moving 2560 x 1440p (2K) resolutions without messing up and even the highly demanded 3840 x 2160p (4K) with some ease.
Components that come installed on a motherboard
Today's motherboards have tons of functionality and at the same time have a multitude of installed components that in the past could only be found on expansion cards. Among them we find:
- BIOS: BIOS or Basic Input-Output System es una memoria de tipo Flash que almacena a small program with information about the configuration of the motherboard and the devices connected to itas well as the devices connected to it. Today BIOS is called UEFI o EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) which is simply a much more advanced BIOS update, with a high level graphical interface, greater security, and a much more advanced component control connected to the motherboard.
- Sound card: When we buy a motherboard, 99.9% of them will have a pre-installed chip that is responsible for processing the sound of our computer. Thanks to him we will be able to listen to music and connect headphones or a Hi-Fi device to our PC without having to buy an expansion card. The most widely used sound cards are Realtek, high quality and diverse outputs for surround sound and microphones.
- Network card: in the same way, all motherboards also have a chip that manages the network connection of our PC, as well as the respective port to connect the router cable to it and have Internet connection. The most advanced also have WiFi connection in them. To understand if it comes with Wi-Fi we will have to identify the 802.11 protocol in its specifications.
- Expansion slots: they are the key to motherboards, in them we will be able to install the RAM memories, graphic cards, hard drives and other ports or connections of our PC. In each of the component we will see these slots in more detail.
The chipset and socket
As we said before, not all base bales are compatible with all processors, what's more, each processor manufacturer will need its own motherboard so that this element can work. For this, each plate will have a socket or plinth different, and only certain processors can be installed in it according to their architecture and generation.
Socket:
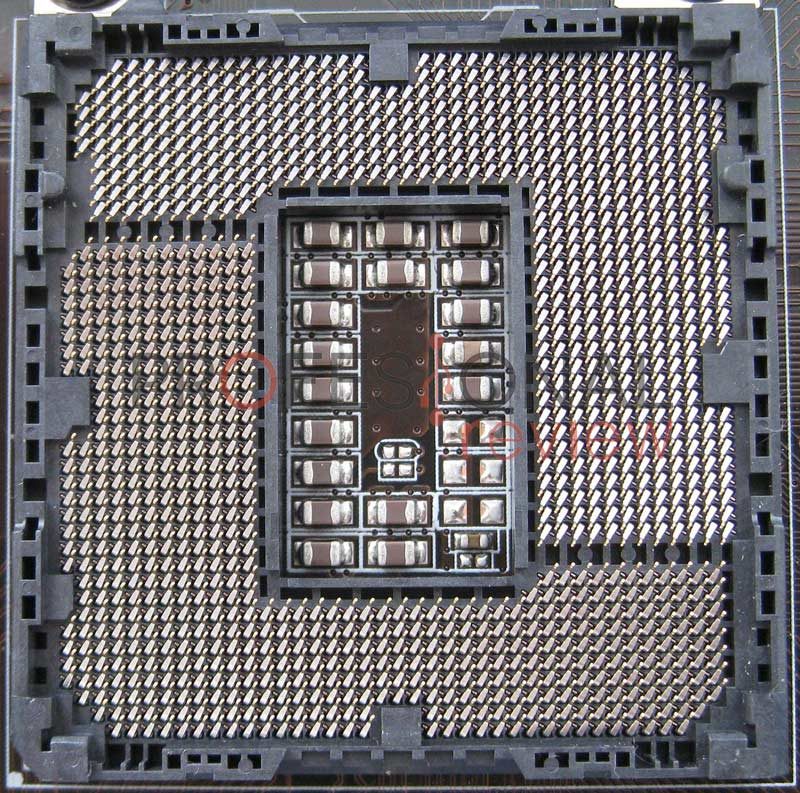
The socket is simply the connector that serves to communicate the processor with the motherboard. It is nothing more than a square surface filled with small contacts that receive and send data to the CPU. Each manufacturer (AMD and Intel) has a different one, and therefore each motherboard will be compatible with certain processors.
Today there are many types of socket for each manufacturer, but these are the ones used in the most current models:
| Intel sockets | |
| LGA 1511 | Used by Intel Skylake, KabyLake, and CoffeeLake architecture. We have mid-range and high-end processors. |
| LGA 2066 | Used for SkyLake-X, KabyLake-X processors and SkyLake-W servers. They are the most powerful processors of the brand. |
| AMD sockets | |
| AM4 | Compatible with AMD Ryzen 3, 5 and 7 platform. |
| TR4 | Designed for the huge AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors, the most powerful of the brand. |
Chipset:
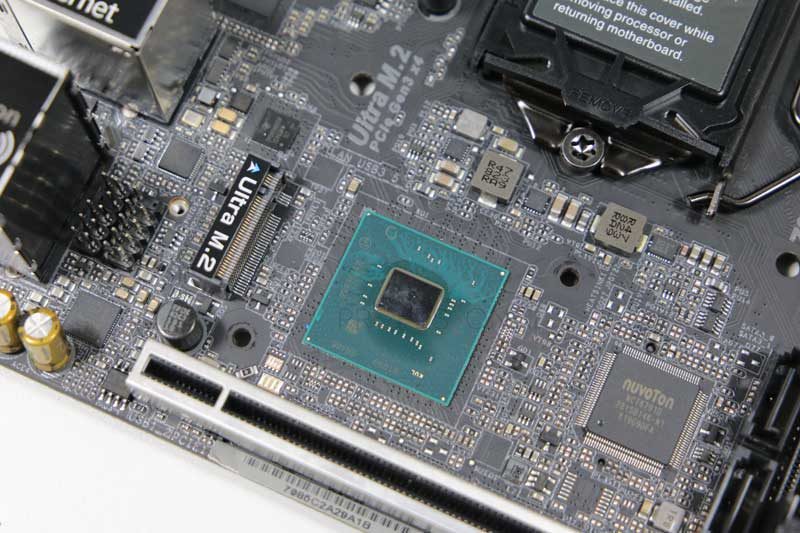

On the motherboard there is also an element called chipset, which is simply a set of integrated circuits that perform the functions of bridge to communicate input and output devices with processor. On older boards, there were two types of chipsets, the north bridge tasked with connecting the CPU with memory and PCI slots, and the south bridge tasked with connecting the CPU with I / O devices. Ahnow we only have a south bridge, Given the the north bridge is included by the current processors inside.
The most important specification of a chipset is the LANES PCI that you have. These LANES or lines are the data paths that the chipset can support, the greater the number of them, the more simultaneous data can flow to the CPU. Connections such as USB, PCI-Express slots, SATA, etc., have a number of LANES if the chipset is small, there will be fewer data lines and fewer devices we will be able to connect or they will go slower.
Cara manufacturer has a range of chipsets that are compatible with their processors, and in turn there will be different models of high, medium and low end, depending on the capacity and speed they have. Now we will cite the Intel and AMD chipsets for the next generation processors.
| Best Intel chipsets | |
| B360 (Socket LGA 1511) | For boards with processors that cannot be overclocked, regularly for mid-range equipment |
| Z390 (Socket LGA 1511) | It is indicated for processors that can be overclocked (Intel K range). For mounting mid-high-end equipment |
| X299 (Socket LGA 2066) | Intel's most powerful chipset for very powerful and high-performance processors |
| Best AMD chipsets | |
| B450 (Socket AM4) | It is the mid-range chipset from AMD, for less powerful equipment even when with the opportunity of overclocking |
| X470 (Socket AM4) | Higher performance chipset, more LANES and capacity for more connectivity and overclocking. |
| X399 (Socket TR4) | The best AMD chipset, for the high-end Ryzen Threadripper |
RAM memory
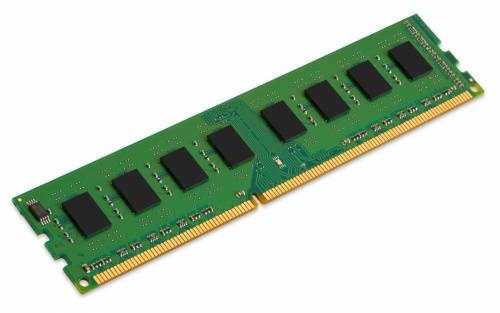
RAM memory (Random Access Memory) is an internal component that is installed on the motherboard and serves to load and store all the instructions that are executed in the processor. These instructions are sent from all the devices connected to the motherboard and to the ports of our equipment.
RAM memory has direct communication with the processor so that the data transfer is faster, even though this data will be stored by the cache memory before reaching the processor. It is called random access because the information is stored dynamically in the cells that are free, in no apparent order. At the same time, this information is not permanently recorded like a hard drive, but it gets lost every time we turn off our PC.
From RAM we must know simply four characteristics, the amount of memory in GB that we have and that we must install, the RAM memory type, its speed, and the groove type that they use depending on each team.
RAM memory type and speed
First, we will look at the types of RAM that are used at the moment and why their speed is essential.
To begin, we must identify the type of RAM that our equipment requires. This is a simple task, since if we have a PC less than 4 years old, we will be 100% sure that it will support DDR type memory in version 4, in other words, Ddr4.
The memories of technology DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic-Access Memory) are those that have been used in recent years in our PCs. Simply the updates of this technology from version 1 to the current version 4, it is about increase frequency of bus considerably, storage capacity and reduce voltage of work to achieve better efficiency. Today we have modules capable of working at 4600 MHz and a voltage of only 1.5 V.
Amount of storage and installation slot of a RAM memory

We continue to see the capacity of RAM memory modules to store information. Due to the evolution of your storage amount, capacities are measured in Gigabytes or GB.
Current memory modules have a capacity that goes from 2 GB up to 16 GB, even though some 32 GB are already being manufactured in test form. The capacity of RAM memory that can be installed in our PC will come limited, so much by the number of slots that has the motherboard, as per the amount of memory that the processor can address.
Intel processors with socket LGA 1511 and those of AMD with socket AM4, are capable of addressing (requesting information from memory cells) up to 64 GB of DDR4 RAM, which will be installed in a total of four modules of 16 GB each in four slots, of course. On the other hand, the plates with sockets Intel LGA 2066 and AMD LGA TR4, they will be able to address up to 128 GB of DDR4 RAM installed in 8 slots with 16GB modules in each.
The installation slots, on the other hand, are simply the connectors on the motherboard where these RAM memory modules will be installed. There are two types of slots:
- DIMM: These are the slots that have the base plates of the desktop computers (the desktop ones). It is used for all DDR memories, 1, 2, 3, 4. The data bus is of 64 bit in each slot and can have up to 288 connectors for DDR4 memory.
- SO-DIMM: These slots are similar to DIMMs, but much smaller, because it is used to install memories in the Laptops and servers, where space is more limited. With regard to performance, they are the same as the DIMM slots and have the same memory capacity and the same bus.
Dual Channel and Quad Channel

Another very important aspect of RAM memory to pay attention to is its ability to work in Dual Channel or Quad Channel.
This technology is simply that the processor will be able to simultaneously enter two or four RAM memories. When Dual Channel is active, instead of entering 64-bit blocks of information, we will be able to access blocks up to 128 bits, and in the same way to 256-bit blocks on Quad Channel.
HDD
We now go on to see the hard drives and the utility they have for our team. Like the previous ones, it is a device that install internally in our team, even when they also exist externally, and connected via USB in most cases.
The hard disk will be the component in charge of alpermanently store all data that we download from the Internet, documents and folders that we have created, images, music, etc. And most important of all, is the element that has the operating system installed with which we can make our PC work.
There are several types of hard drives, as well as build technologies, you've heard of HDD hard drives or SDD hard drives, therefore let's see what they consist of.
HDD hard drive

These hard drives are the ones that have always been used in our computers. It is a rectangular metal device of considerable weight that stores a series of discs or plates stuck on a common axis. This axis it has a motor to make them turn at high speeds and it will be feasible to read and write information thanks to a magnetic head located on the face of each plate. Exactly for this system, they are called mechanical hard drives, since it has motors and mechanical items inside.
The discs have two useful faces in which to save information through zeros and ones. These are logically divided into tracks (concentric ring of a disk), cylinders (set of tracks aligned vertically on the various decks) and sectors (pieces of arch into which the tracks are divided).
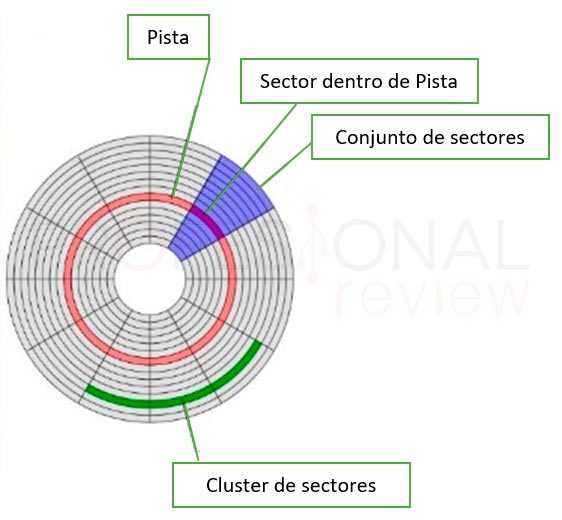
The important thing about hard drives is their Storage capacity and speed they have. Capacity is measured in GB, the more you have, the more data we can store. Today we find for sale hard drives of up to 12 TB or up to 16, which would be 16,000 GB. With regard to sizes, we simply have two types of discs:
- 3.5 inch disk: they are the traditional ones, the ones used by desktop PCs. The measurements are 101.6 × 25.4 × 146 mm.
- 2.5 Inch Disc: they are the ones used for portable PCs, smaller and with less capacity. Its measurements are 69.8 × 9.5 × 100 mm.
SATA is the connection interface that use these hard drives to connect to our PC through a connector on the motherboard. The current version is SATAIII or SATA 6Gbps, because this is the amount of information that is capable of being transmitted per unit of time. 6 Gbps is approximately 600 MB / s, it seems like a lot, but it is nothing compared to what we will now see. Anyway, a mechanical hard drive is not able to reach this speed, at most meets 300 MB / s.
Hard Drive SSD

It is not correct to call hard drives, since the storage technology is very different from that used by HDDs. In this circumstance we must make solid state storage drives, which are devices capable of permanently storing information in flash memory chips, such as those available in RAM memories. In this circumstance the data is stored in memory cells formed by NAND logic gates simply, since they can store a voltage state without the need for a current supply. There are three types of manufacturing technologies, SLC, MLC and TLC.

These units they are much faster than HDD, because inside there are no mechanical items or motors that take time to move and place the head on the proper track. Today these are used types of technologies connection for SSDs:
- SATA: it is the same interface that is used in the HDD, but for this case the 600 MB / s that it is capable of transmitting. Therefore, from the outset, they are already faster than mechanical discs. These drives will be encapsulated in 2.5-inch cabinets.
- 2 with PCI-Express: it is simply a slot located on our motherboard that uses an interface PCI-Express x4 under the NVMe communication protocol. These units are capable of speeds up to 3,500 MB / s in reading and writing, impressive undoubtedly. These drives will simply be uncapsulated expansion cards, looking like RAM.
- 2: is another new connector that also uses an interface PCI-Express x4. These units will also be encapsulated.
Of course you have two guides to see and compare the latest models available on the market:
Graphic card
This component is not strictly necessary to be installed on our PCs, at least in most cases, and now we will see why.
A graphics card is simply a device that It is connected to a PCI-Express 3.0 x16 expansion slot that has a graphics processor or GPU which is responsible for all the complex graphics processing of our PC.
We say that they are not strictly essential because most processors current they have a circuit inside what is able to handle the processing of this graphic data, and that is why motherboards have HDMI or DisplayPort ports to connect our screen to them. These processors are called APU (Accelerated processing unit)
So why do we long for a graphics card? Simple, because the graphics processor of a card is much more powerful than that of processors. If we long to play games, we will almost obligatory need a graphics card in our equipment.
Graphics card manufacturers and technologies
There are basically two graphic card manufacturers on the market Nvidia and AMD and each of them has different manufacturing technologies, even though today Nvidia has the best graphics cards on the market for being more powerful.
Nvidia

Nvidia has the best graphics cards out there today, they may not be the cheapest, but they do have the highest performing models on the market. There are simply two Nvidia graphics card manufacturing technologies:
- Turing technology: it is the most current technology with 12nm GPU and video memories GDDR6 capable of transfer speeds of up to 14 Gbps. These cards are capable of performing real-time ray tracing. In the market you will be able to identify these cards by the model GeForce RTX 20x.
- Pascal technology: it is prior to Turing, and they are cards that use the manufacturing procedure of 12 nm and memories GDDR5. We will achieve them identifies by their name GeForce GTX 10x.
AMD

It is the same processor manufacturer which is also dedicated to building graphics cards. Their TOP models do not have the overwhelming power of the top-of-the-range Nvidia, but it also has very practical models for most players. It also has several technologies:
- Radeon VII: It is the newest technology of the brand, and it comes with the newly released AMD Radeon VII card with a manufacturing procedure of 7 nm and memory HBM2.
- Radeon vega: it is the current technology and that at the moment is on the market with two models, Vega 56 and Vega 64. The manufacturing procedure is 14 nm and using HBM2 memories.
- Polaris RX: It is the previous generation of graphics cards, relegated to mid-range and low-end models, even when with very good prices. We will identify these models by the different Radeon RX.
What is SLI, NVLink and Crossfire
Along with the manufacturing technology and the characteristics of the GPUs and memory of the graphics cards, it is essential to know these three terms. We are simply referring to the ability of a graphics card to connect with another precisely the same to work together.
- The SLI technology and the most current, NVLink, he uses it Nvidia to be able to connect two, three or four graphic cards that work in parallel in PCI-Express slots. For this, these cards will be connected with a cable on the front.
- For its part the crossfire technology belonging to AMD, and also serves to connect up to 4 AMD graphics cards in parallel, and a cable will also be necessary to make the connection.
This method is not widely used, due to the cost, and it is only used by extreme configurations of PC's used to play games and to perform data mining.
Power supply

Another of the components of a PC that are necessary for the operation of this is the power supply. As its name suggests, it is a device that provides electrical current to electronic items that constitute our PC, and that are simply those that we have already seen in previous sections.
These sources take care of transform alternating current from our 240 Volt (V) house in direct current and distribute it among all the components that need it through connectors and cables. Regularly the tensions that are handled are of 12V and 5V.
The most important measure from a power supply or PSU is the powerThe more power, the greater the ability to connect items this source will have. Typically, a font on a desktop PC with a graphics card is at least 500 WSince, depending on what processor and motherboard we have, they can consume about 200 or 300 W. Likewise, a graphics card, depending on which one, will consume between 150 and 400 W.
Types of power supplies.

The power supply will go inside the chassis, along with the other internal components. There are different PSU formats:
- ATX- This is a normal size font about 150 or 180mm long by 140mm wide by 86mm high. It is compatible with boxes named ATX and the vast majority of boxes Mini-ITX and Micro-ATX.
- SFX: they are smaller fonts and specific for Mini-ITX boxes.
- Formato de server: they are sources of special measures and that are incorporated in the server boxes.
- External power supply: They are the traditional transformers that we have for our laptop, printer or video game consoles. That black rectangle that is always lying on the ground is a power source.
Connectors of a power supply
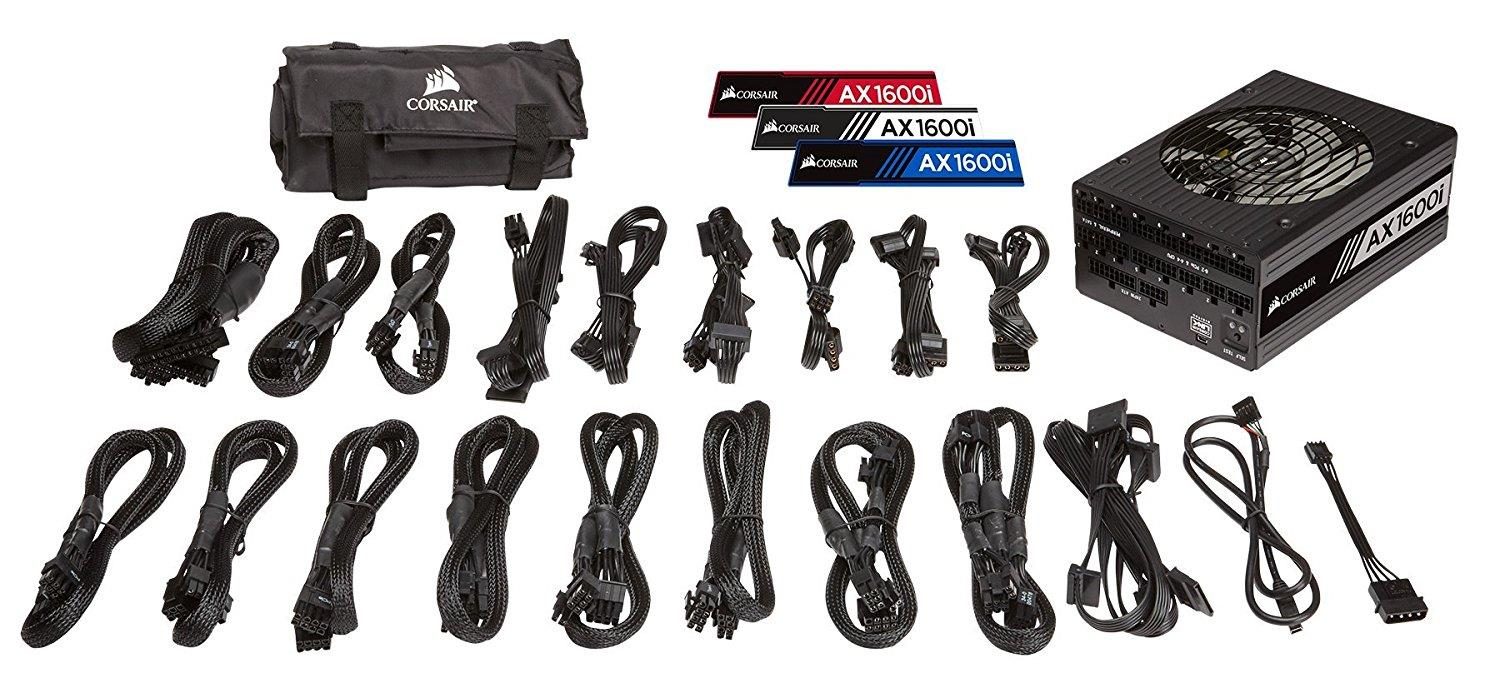

The connectors of a source are very important and it is worth knowing them and knowing what each of them are used for:
- 24-pin ATX: This is the main power cable of the motherboard. It's very wide and has, that, 20 or 24 pins. It carries different voltages in its cables.
- EPS 12V- This is a cable that carries direct power to the processor. This is a 4-pin connector, even though they always come in 4 + 4 format that can be separated.
- PCI-E connector- Used to regularly power graphics cards. It is very similar to the EPS of the CPU, but for this case we have a 6 + 2 pin connector.
- SATA power: We will identify it by having 5 cables and be an elongated connector with a slot in the form of "L".
- Molex connector: This cable is used for the old mechanical hard drives connected by IDE. It consists of a connector four poles.
Network card

Very certainly you do not have this component as such visible on your PC, since, in all cases, our motherboard already has a built-in network card.
A network card is an expansion card, or internal to the motherboard that will allow us connect to our router to get internet connection or to a LAN. There are two types of network cards:
- Ethernet: with a connector RJ45 to introduce a cable and connect to a wired network and LAN. A normal network card provides a connection with transfer speeds on a LAN network of 1000 Mbit / s, even though there are also 2.5 Gb / s, 5 Gb / s and 10 Gb / s.
- Wifi: we also have the card, a wireless connection will be provided to our router or to the Internet. It is installed by portable PCs, our Mobile Device and many motherboards.
If we yearn to get an external network card, we will need a slot PCI-Express x1 (the little one).
Heatsinks and liquid cooling
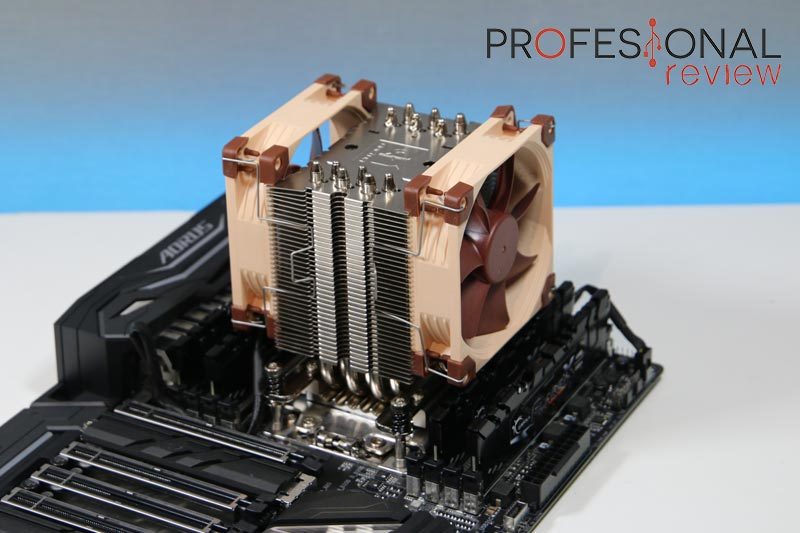
Finally, we must mention as components of a PC the heatsinks. They are not strictly necessary items for a PC to work, but its absence can cause a PC to stop working and break.
The mission of a heatsink is very simple, collect the heat generated by an electronic element as a processor due to its high frequency and transmit it to the environment. To do this a heatsink consists of:
- A metal block, regularly copper which is in direct contact with the processor through a thermal paste that helps heat transfer.
- An aluminum block or exchanger formed by a large number of fins through which air will pass so that the heat from them is transmitted to it.
- Some heat pipes copper or Heatpipes that will go from the copper block to the entire finned block so that the heat is transmitted to this entire surface in the best way.
- One or various fans so that the air flow in the fins is forced and thus eliminates more heat.
There are also dissipators in other items such as the chipset, power phases and decidedly in the Graphic card. But there is a higher performance variant called liquid refrigeration.
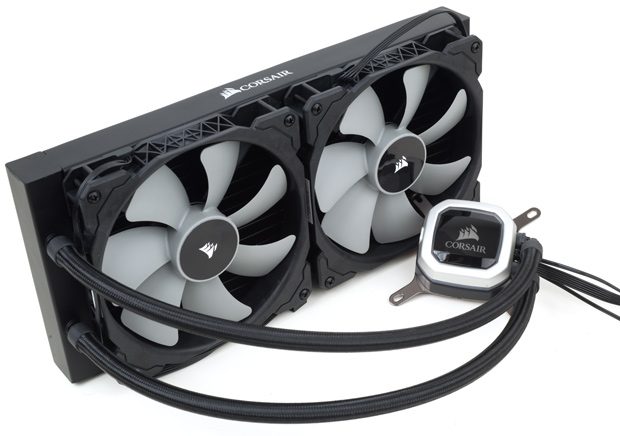

Liquid cooling is about separating the dissipation items into two large blocks that make up a water circuit.
- The first one will be located in the processor itself, it will be a copper block full of small channels through which a liquid will circulate powered by a pump.
- The second will be a finned exchanger with fans that will be responsible for collecting the heat from the water that reaches it and transmitting it to the air.
- For this you should use a series of tubes that make up a circuit in which the water circulates and never evaporates.
The chassis, where we keep all the components of a PC

The chassis or box is a enclosure constructed of metal, plastic and glass who will take care of store this entire ecosystem of electronic components and thus have them ordered, correctly connected and refrigerated. We must always know about a chassis what motherboard format does it support to install them, and its dimensions to see if all of our components will fit in it. In this way we will have:
- Chassis ATX or Mid-tower- This is a case that is approximately 450mm long, another 450mm high and 210mm wide. It is called ATX because we will be able to install motherboards in ATX format and also smaller ones. They are the most used.
- E-ATX chassis or full tower: They are the largest and are capable of housing practically any component and motherboard, even the largest.
- Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX or mini tower box: they are of a smaller size, and they are designed to be able to install the motherboards of these types of formats.
- SFF box: These are the typical ones that we find in the PC's of the universities, they are very thin towers and that are placed in cabinets or lying on a table.
The tower will be the most visible element of our PC, therefore manufacturers always strive to make them as impressive and bizarre as possible so that the result is spectacular.
These are all the basic components of a PC and the keys to knowing its operation and the types that exist.
We also suggest these tutorials with which you will learn everything you need to assemble your own computer and know the compatibility of its components.
We hope this post has clarified what the main components of a PC are.