The SWOT analysis is a strategic management technique used to help people or companies identify the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats related to business competition and project planning.
Definition
The expression SWOT (SWOT analysis in English) is composed of the acronyms of the words: Weaknesses, Threats, Strengths and Opportunities. The Strengths and Weaknesses correspond to internal factors while the Opportunities and Threats, to external ones.
objective
With the help of SWOT analysis (or SWOT), you can develop strategies, define budgets and make the most of resources. At the same time, strategic planning can help initiate business action and enable informed decisions. The SWOT in addition, it is often necessary in the course of a company analysis for the preparation of business plans, for the financing of newly created companies, for the control or increase of the capital of the companies.
Internal factors
In order to identify your own strengths and weaknesses, it is necessary to review the situation of your competitors and compare the data obtained from the previous analysis with the data of your company. This is the simplest way to discover in which aspects your company is a leader and in which others it is not, in order to be able, therefore, to define the strengths and weaknesses.
Strengths
Strengths are those characteristics of a company that position it in an advantageous situation in relation to its competitors and can be found with the USP analysis. That is, they are aspects that allow the company to point out its competitors:
- Low fixed costs
- Highly qualified employees
- Use cross-selling, or cross-selling.
- Use the upselling as a Marketing strategy
- Good infrastructure
- Innovative products
- Advanced technical knowledge
- Employee loyalty
- High quality products
- Flexibility in the face of market changes
- Horizontal organizational structure and short decision processes
To identify strengths, you need to check how successful situations have been achieved in the past, and what are the differences between your company and your competitors.
Weaknesses
The weaknesses of a company are the characteristics that could put it at a disadvantage compared to its competitors. Possible examples are:
- Dependence on a provider
- Reduced clientele
- Bad sales position
- Low quality
- High prices
- Outdated IT system
- Very frequent changes in staff
- Low brand awareness
To discover what your weaknesses are, you can ask yourself the next question: Why have my potential customers preferred to buy from my competitors and not from me?
External factors
In this chapter of the SWOT factors external to the company are analyzed. This external analysis helps the company to know opportunities and threats that may be present in the future. Some examples are: changes in the markets, legal changes and changes in trends.
Opportunities
Opportunities are external changes that could turn into advantages for the company. Some examples are:
- Change in trends and development of society
- Changes in consumer behavior
- Technological progress
- Market niches
- Great market potential
- New distribution channels
Threats
Threats are external changes that can become disadvantages for a company. For example:
- Negative legal changes for the company
- Negative changes in the stock market or in exchange rates
- New Competitors
- Cheaper competitors (from very low-wage countries)
- Fall in prices due to excess supply
- Little economic activity
Analysis process
To carry out a SWOT analysis, it is necessary to carry out an internal analysis (company analysis) and external (environmental analysis) of the company.
Company analysis
It is about reviewing the company internally. Discover the strengths and weaknesses that lead to advantages or disadvantages from a competitive point of view. It is also known as internal analysis.
For this, we will have to ask ourselves the following questions:
Strengths:
- What decisions that have been made in the past have been successful?
- What have been the deciding factors of success so far?
- What are the strengths of the company / product?
Weaknesses:
- What went wrong in the past?
- What can't the company / product do as well as the competition?
- What are customers complaining about / What are the reasons for the loss of customers?
All this analysis leads us to ask ourselves questions about the departments of the company:
- Production: costs and manufacturing processes.
- Marketing: sales team, products, positioning, market share, prices, distribution, customer service.
- Organization: organization chart, company culture, senior management.
- Personal: recruiting and compensation procedure, employee training, team motivation.
- Finance: financial ratios of the company, R&D.
Environmental analysis
The second step of SWOT is to identify the factors that can affect the company in a positive or negative sense. Typical examples are movements in the markets, legal changes or trends. This environmental analysis is also called an exogenous / external factors. To carry out this analysis we must ask ourselves the following questions:
Opportunities:
- What are the real possibilities for growth?
- What are the current trends?
- Where does my competition fail?
Threats:
- Where are there dangers / risks for the company / product?
- What changes in the market can have a negative effect?
- Are there new competitors?
In conclusion, we must look at the environment of our company:
- Market: Define our target audience and its characteristics. Market size, segmentation and supply and demand.
- Sector: Review the environment that surrounds me, as well as the suppliers, or distributors in my sector.
- Competition: conduct an analysis of my current competition. Your prices, positioning and products.
- Environment: factors that surround us that we cannot control (political situation, legal situation ...).
SWOT matrix
Following internal and external analysis, the information is combined in the so-called matrix SWOT. This presentation allows you to quickly identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and risks. The goal is to use existing strengths to compensate for weaknesses and to seize opportunities to offset potential risks.
Strategies
All strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats are presented in an organized way in the SWOT analysis. Connections are created from this dynamics in a very visual way. With these results, strategies are carried out to promote the positioning of the company in the market and define the measures to be taken.
The most important strategies are:
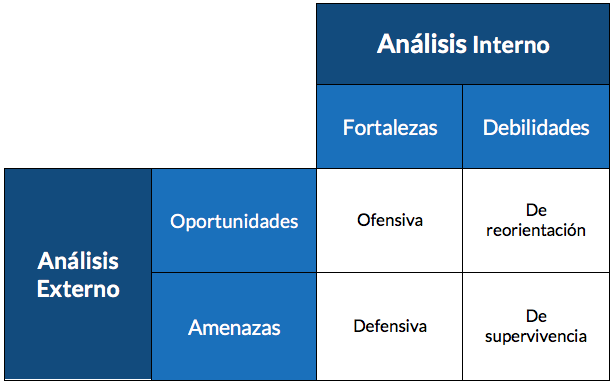
- Offensive strategy: It is the most desired by companies. It combines opportunities and strengths, and is achieved by taking advantage of the environment that surrounds the company, trying to erase all weaknesses and threats.
- Defensive strategy: Refine strengths to minimize threats. With this strategy, companies prepare to better face the future.
- Retargeting strategy: Take advantage of opportunities in the environment to drive weaknesses.
- Survival strategy: It is about avoiding threats and minimizing weaknesses. Therefore, an attempt is made to reduce market threats and at the same time internally reduce weaknesses. This situation should be avoided as much as possible.
Graphically, we can see the strategies in the SWOT Matrix as follows:
Common mistakes
In practice, companies make mistakes that severely limit the importance of SWOT analysis. As a result, sometimes the wrong decisions are made or important changes are not recognized. Typical errors are:
- Subjectivity: not only the selection but also the evaluation of the factors do not follow an objective pattern. There is a risk that important factors are not given enough weight. In addition, strengths and opportunities may be given greater consideration to, at times, justify decisions that have already been made.
- Give little thought to competitors- Although competitors are indeed part of the analysis, they sometimes go unnoticed in the opportunities and threats categories. It is very important to react in time to changes in competitors and the market with appropriate strategies.
- Absence of reference points: there are no standard references that facilitate the evaluation and comparison of the data obtained with this analysis.
- Much effort and time: For the analysis to be important, as much information as possible is required. This takes a lot of time and effort.
critics
The SWOT analysis It has some weak points that question its relevance:
A major criticism is that there is no standard for quantifying and examining the four areas and the strategies derived from them. This leaves the evaluation in the hands of the companies themselves, which can lead to wrong decisions.
Another problem with this analysis is effort: the more data that is available, the more meaningful the SWOT analysis will be. However, obtaining it can involve a very high research effort. So often, companies save time and come up with incomplete analyzes, which in turn are less meaningful.
SWOT analysis in online marketing
In long-term planning of online marketing campaigns, a detailed SWOT analysis in advance can help avoid potential mistakes. But in a dynamic environment such as online, all those involved must be aware that their actions and the measures taken must be readjusted regularly. For example, search engine optimization rules may have changed again since the strategic planning was developed based on the SWOT analysis. For this case, the individual aspects within the matrix may change. Therefore, the model must be updated over and over again when planning for the long term.
Web links
- The SWOT Analysis Matrix (SWOT) Robertoespinosa.es blog
- SWOT analysis for websites Visible Ranking
- SWOT analysis example The fourpes